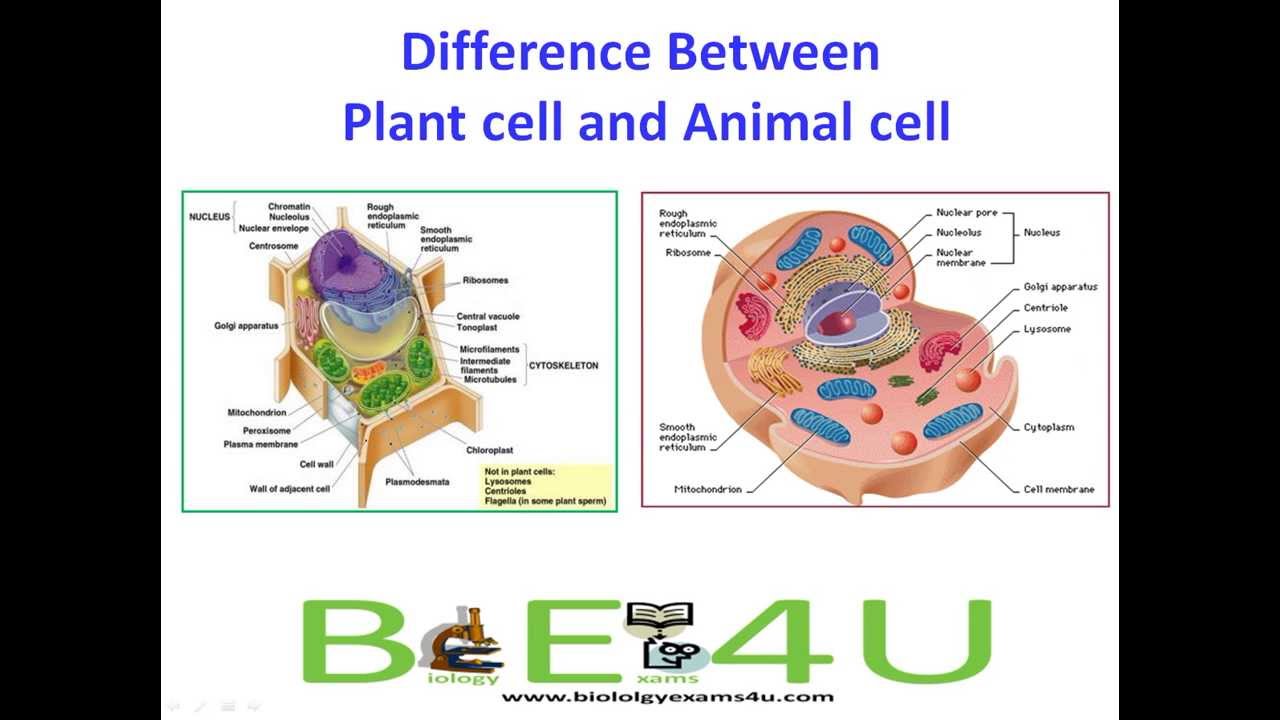
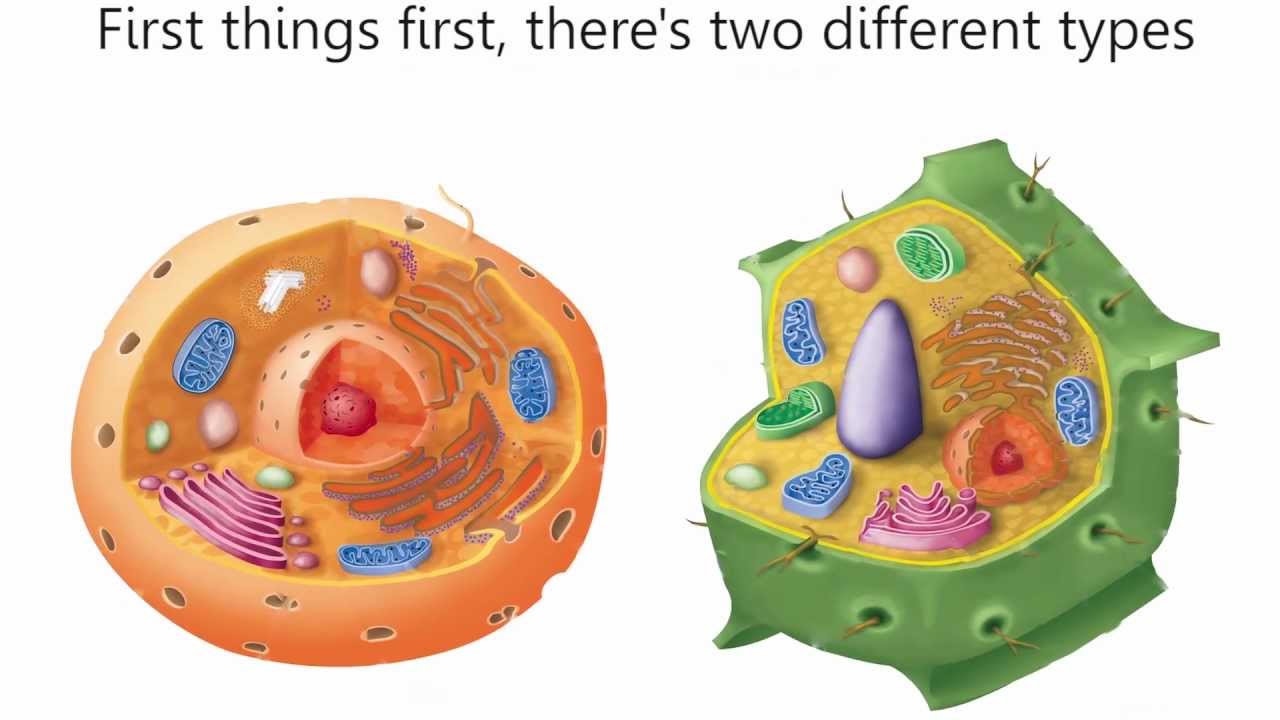
Plants And Animals Cells

Animal cells and plant cells share the common components of a nucleus cytoplasm mitochondria and a cell membrane.
Plants and animals cells. Plant cells are autrotrophs meaning they are able to make their own food while animal cells are heterotrophs meaning they have to take in nutrition from outside sources such as plants or animals. Some of the major organelles include the nucleus mitochondria lysosomes the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Plant cells also include chloroplasts which are responsible for photosynthesis.
The plant cell can also be. The plant cell is rectangular and comparatively larger than the animal cell. Lysosome Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders.
Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. Cytoplasm Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. Nerve cells bone cells and liver cells for example all develop in ways that enable them to better perform.
Both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane but only the former has a cell wall. Plant and animal cells share a lot of common traits but they also have their differences. Nucleus and cell membrane.
Allows materials in and out. Both Respire All cells need energy to grow and function and animal and plant cells both obtain this energy from cellular respiration. Plant cells are generally larger than animal cells as animal cells can be around 10-30 micrometers while plant cells can range from 10-100 micrometers.
Label a plant and animal cell. Chloroplasts are what give plants their green color. In this lesson plan students will explore both the similarities and differences between the two and.