Cellular Respiration Takes Place In Two Stages
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
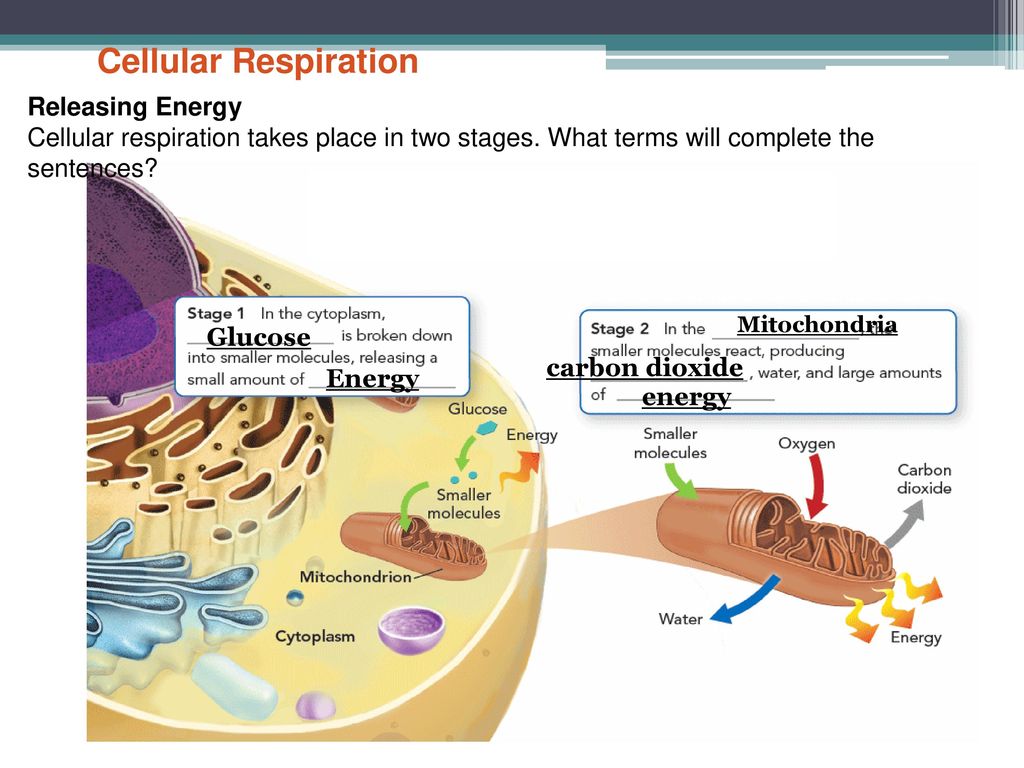
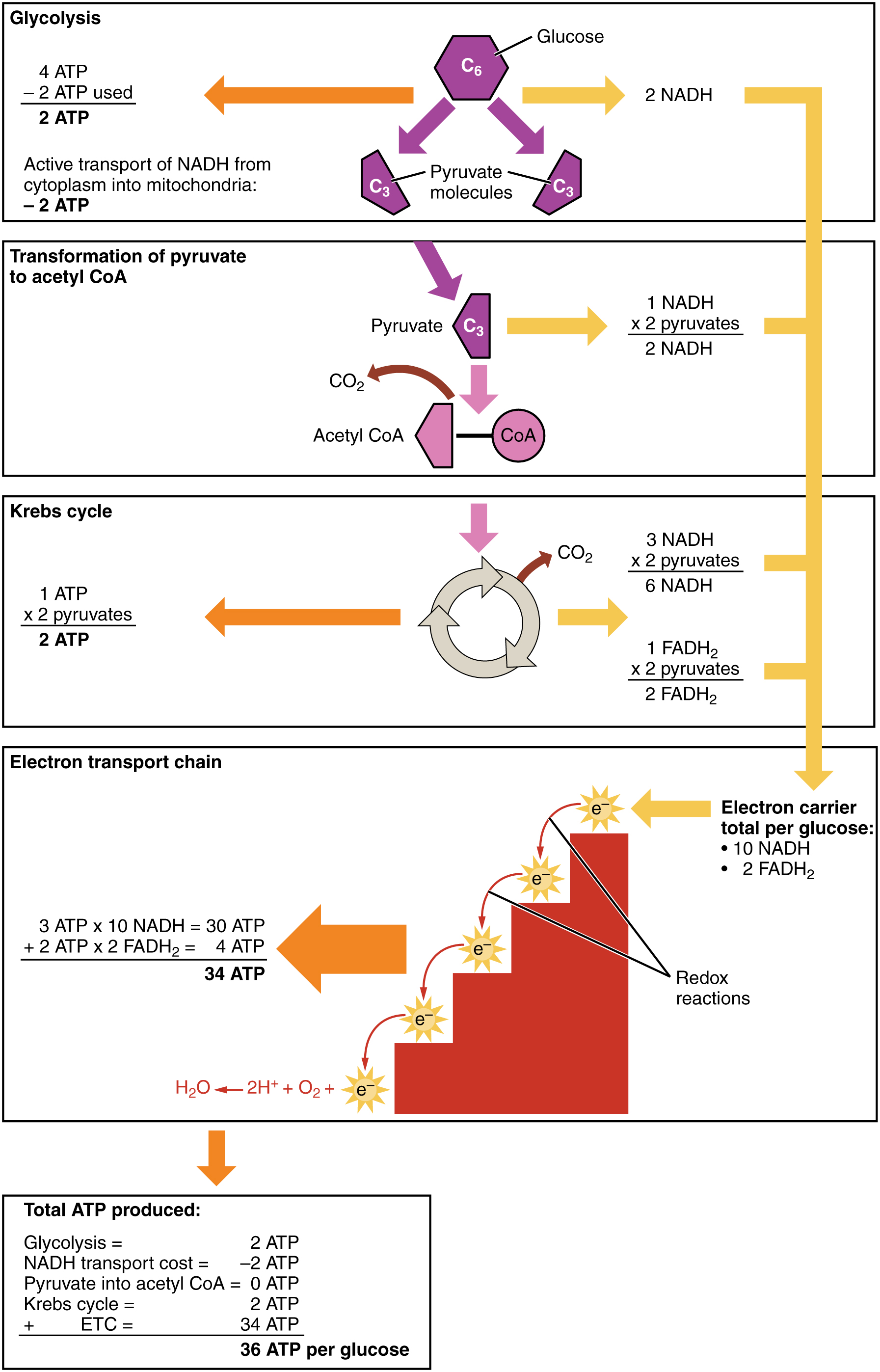
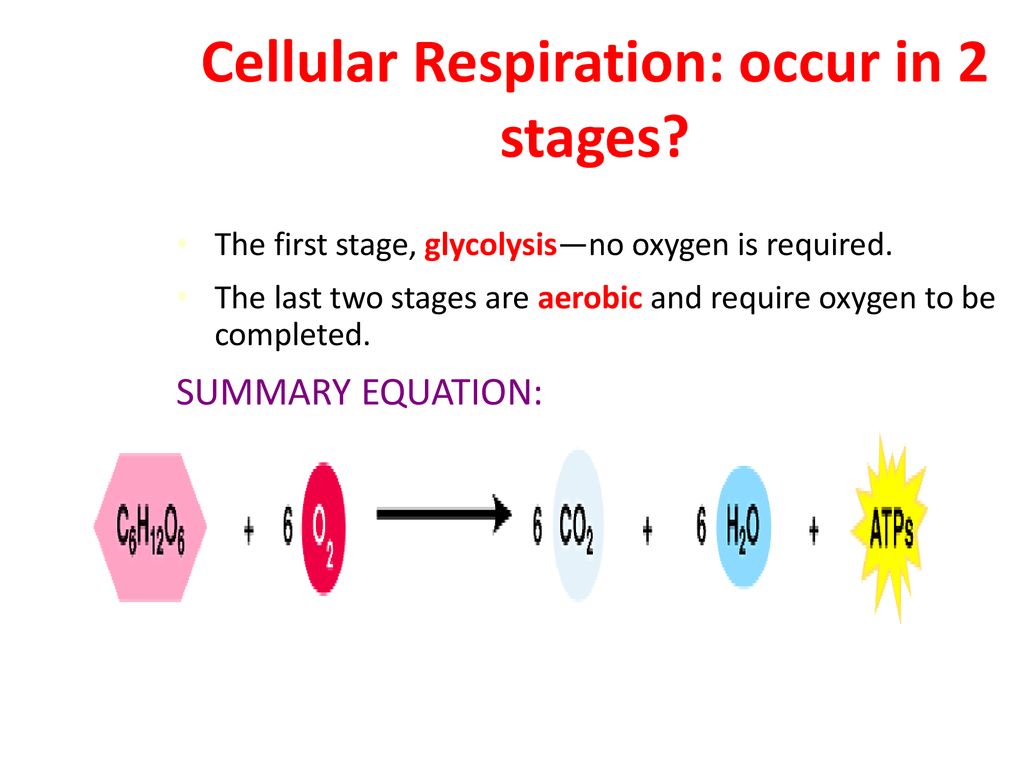
Cellular respiration takes place in two stages. Out of these both internal and cellular respiration occurs at the cellular level. Respiration is of two types aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis is the first pathway in cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration Equation. Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. The three stages of aerobic cellular respiration are.
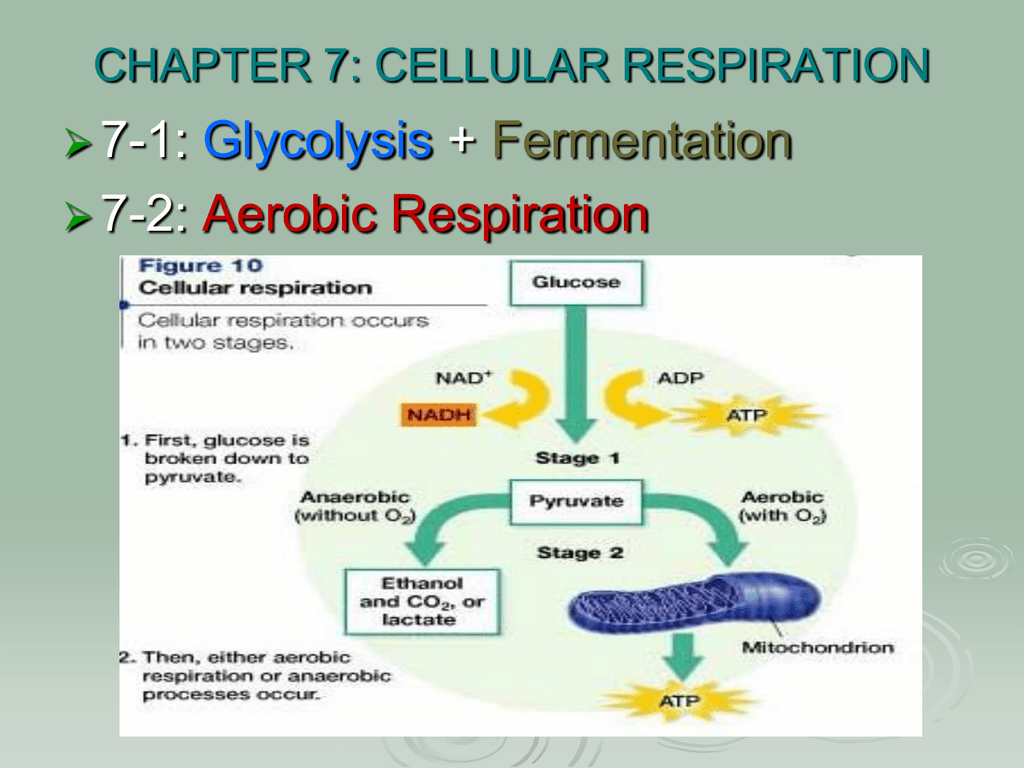
There are two halves of glycolysis with five steps in each half. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cell cytoplasm. The stages in anaerobic respiration are.
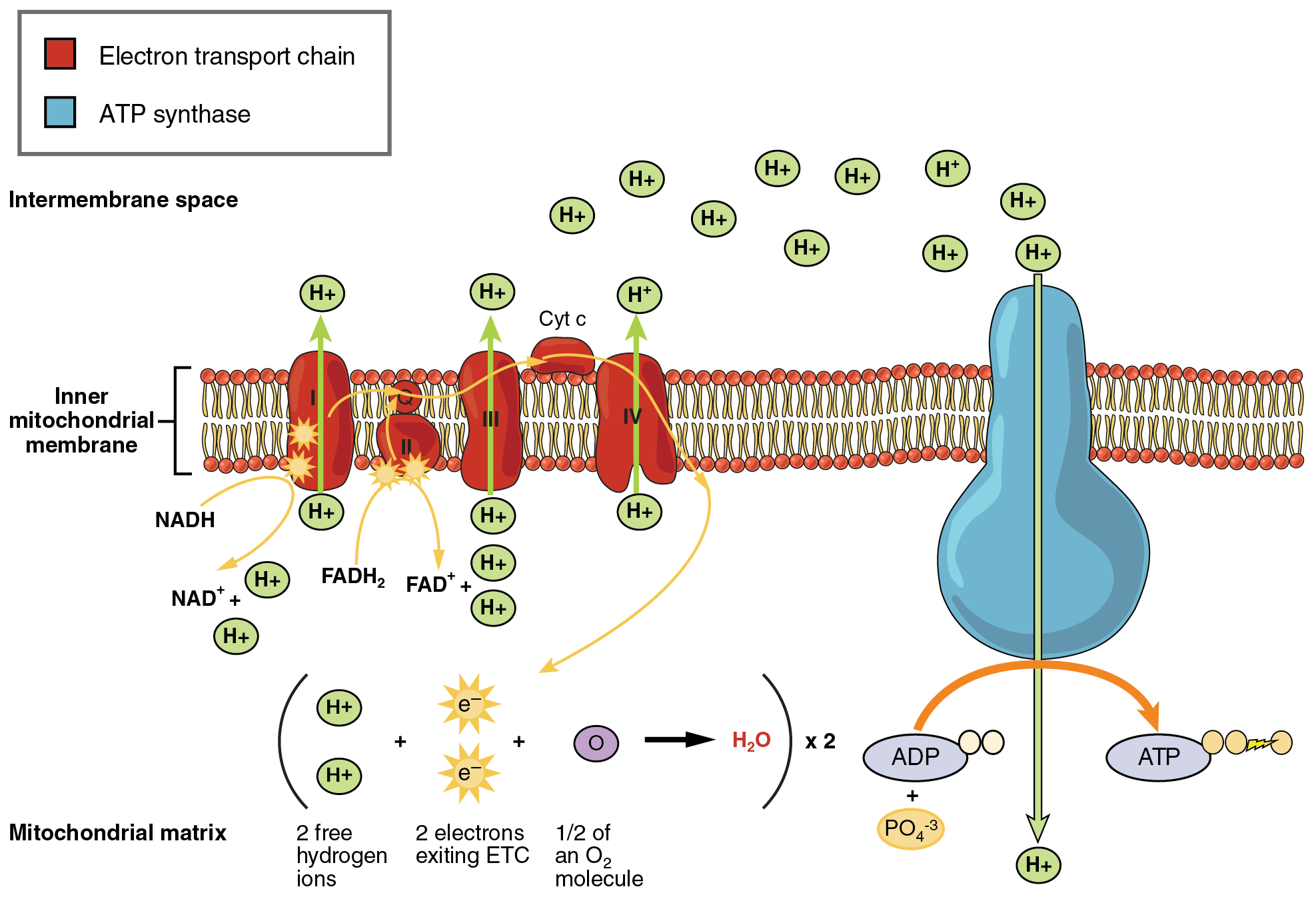
Electron transport and oxidative carboxylation. Needed at the start of glycolysis to split the glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules. This includes the entry of oxygen and the exit of carbon dioxide from the cells.
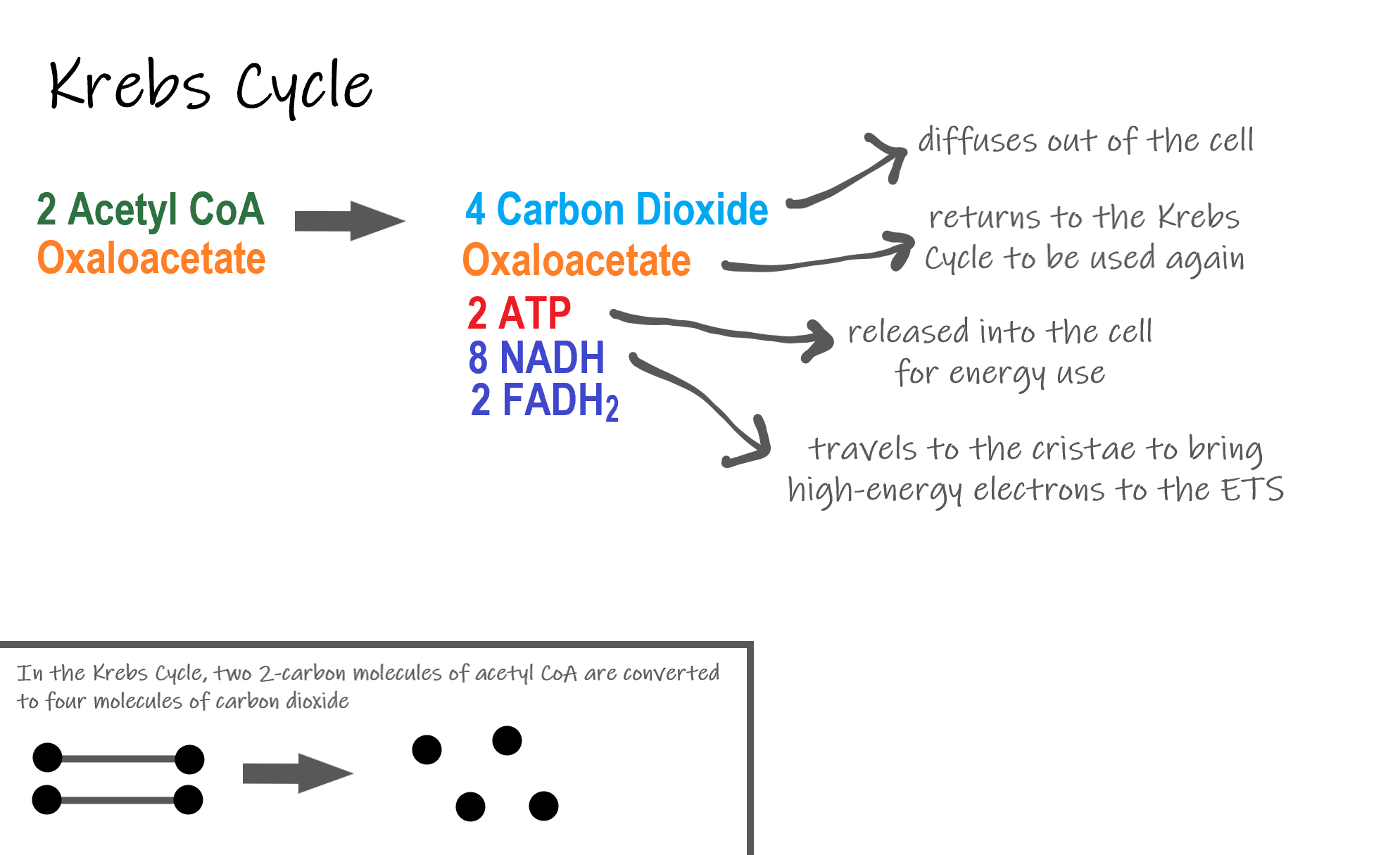
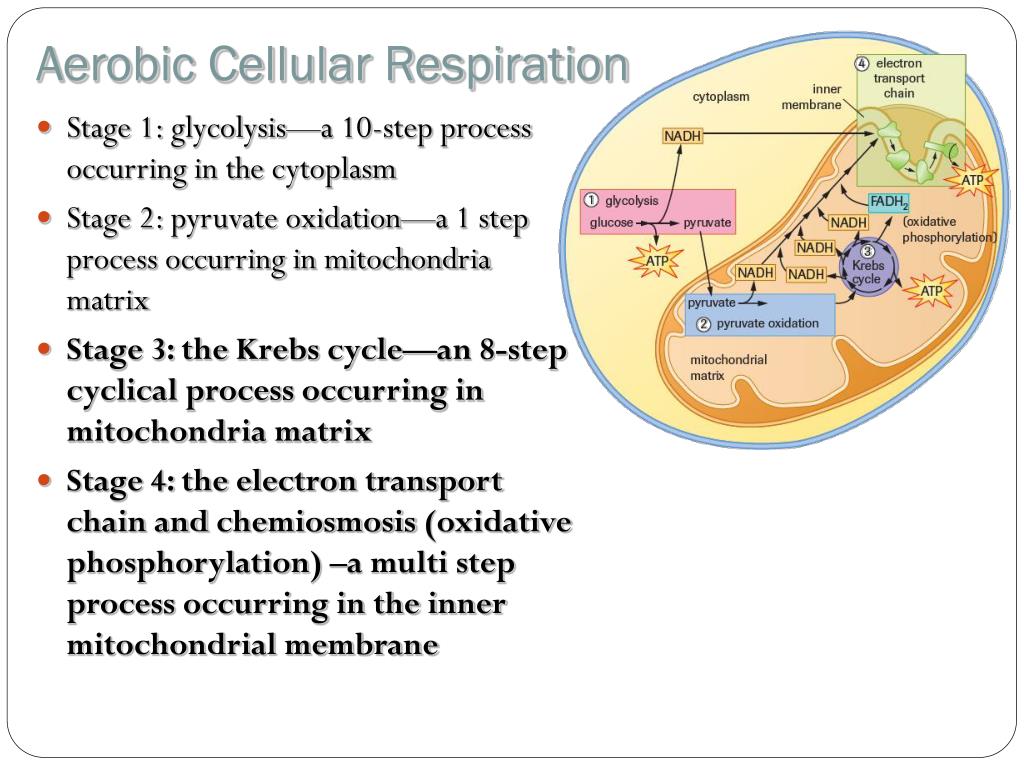
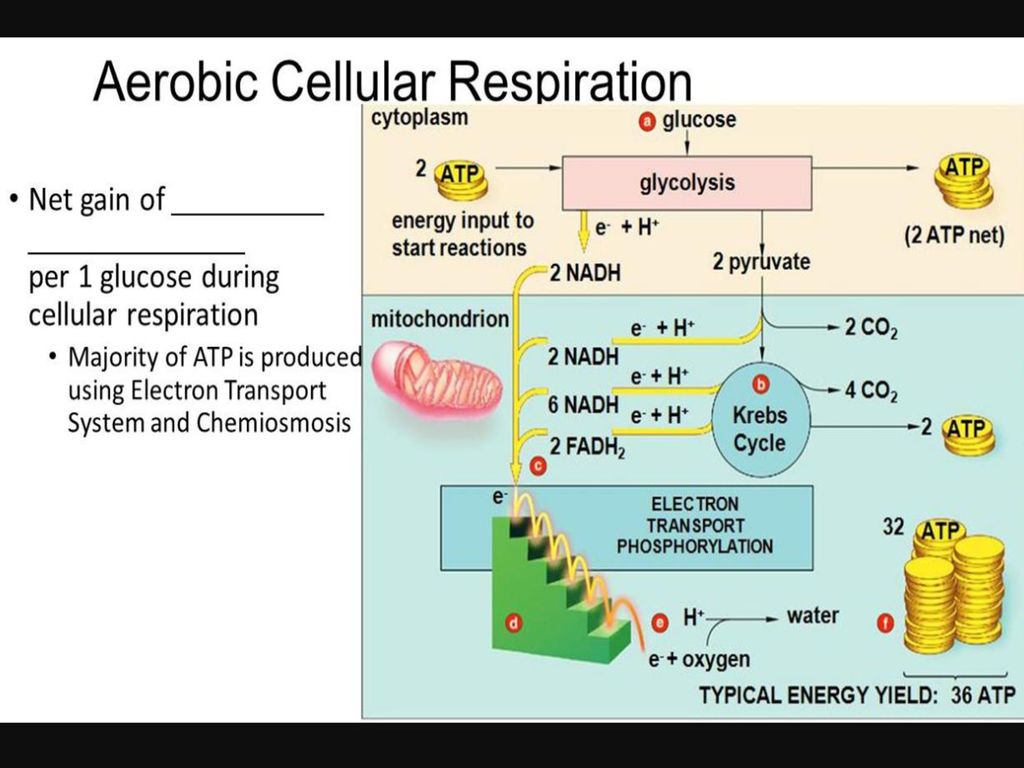
The Krebs Cycle which takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. 2 molecules of ATP are produced in anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic Respiration The first step in cellular respiration in all living cells is glycolysis which can take place without the presence of molecular oxygenIf oxygen is present in the cell then the cell can subsequently take advantage of aerobic respiration via the TCA cycle to produce much more usable energy in the form of ATP than any anaerobic pathway.
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and. Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes.


/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)
