Cellular Respiration Equation Explained

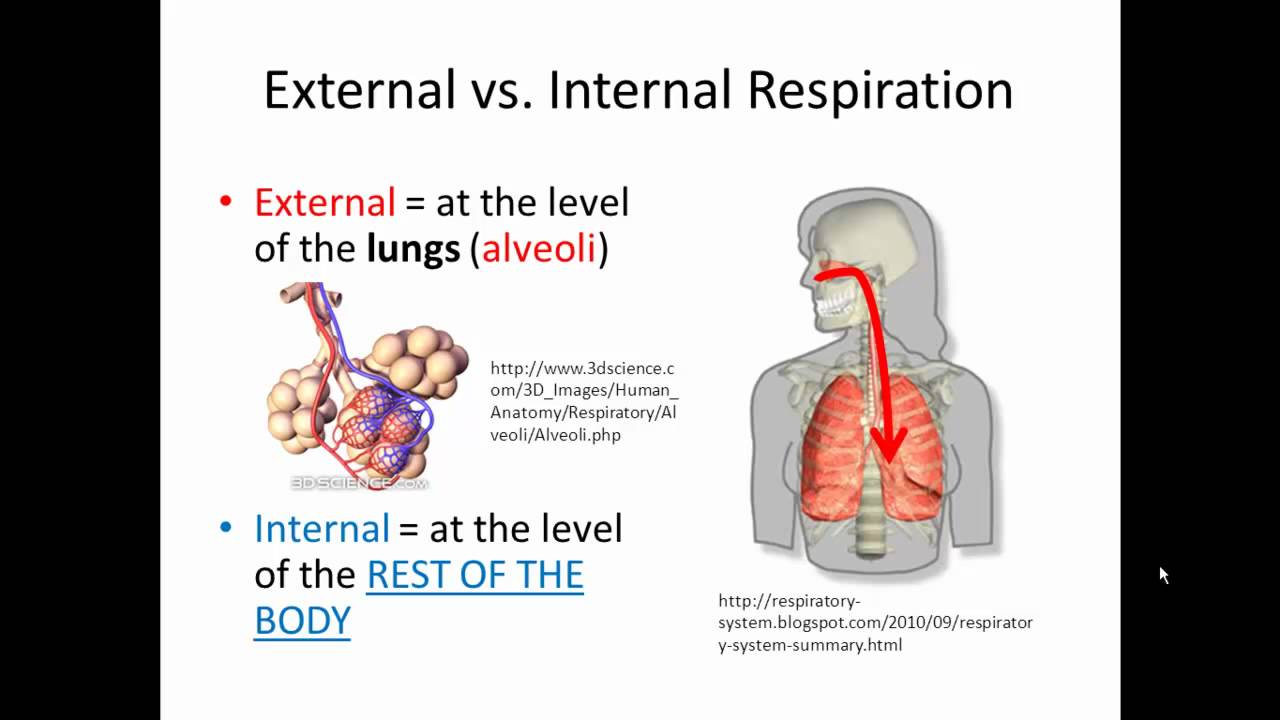
The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen.
Cellular respiration equation explained. Such processes are explained below. The word equation for cellular respiration is glucose sugar oxygen carbon dioxide water energy as atp. This type of respiration is common in most of the.
This is the overall equation. Cellular Respiration Definition. Glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water energy The equation is formulated by combining the three following processes into one.
Cellular respiration formula explained. This is the balanced equation that yields energy. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is.
During cellular respiration a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Along the way some ATP is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O Energy as ATP The word equation for this is.
Cellular respiration formula explained. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration. At the end of the electron transport chain oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water.
Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy. There are two types of electron carriers that are particularly important in cellular respiration. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products.