Cell Membrane Structure Journal
L Thefluid mosaicmodelofthestructure of cell membranes Science 175 18.
Cell membrane structure journal. 3 cholesterol-enriched domains exist in the cell membrane. Ad Reveal the Subcellular Localization in Cell Imaging Applications. View our cryo-EM collection from Structure and Molecular Cell The papers included in the collection showcase how cryo-EM has enabled us to address SARS-CoV-2 biology antimicrobial resistance mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis the architecture and dynamics of integrator complexes ion channels receptors and phage-genome degradation versus host-genome protection.
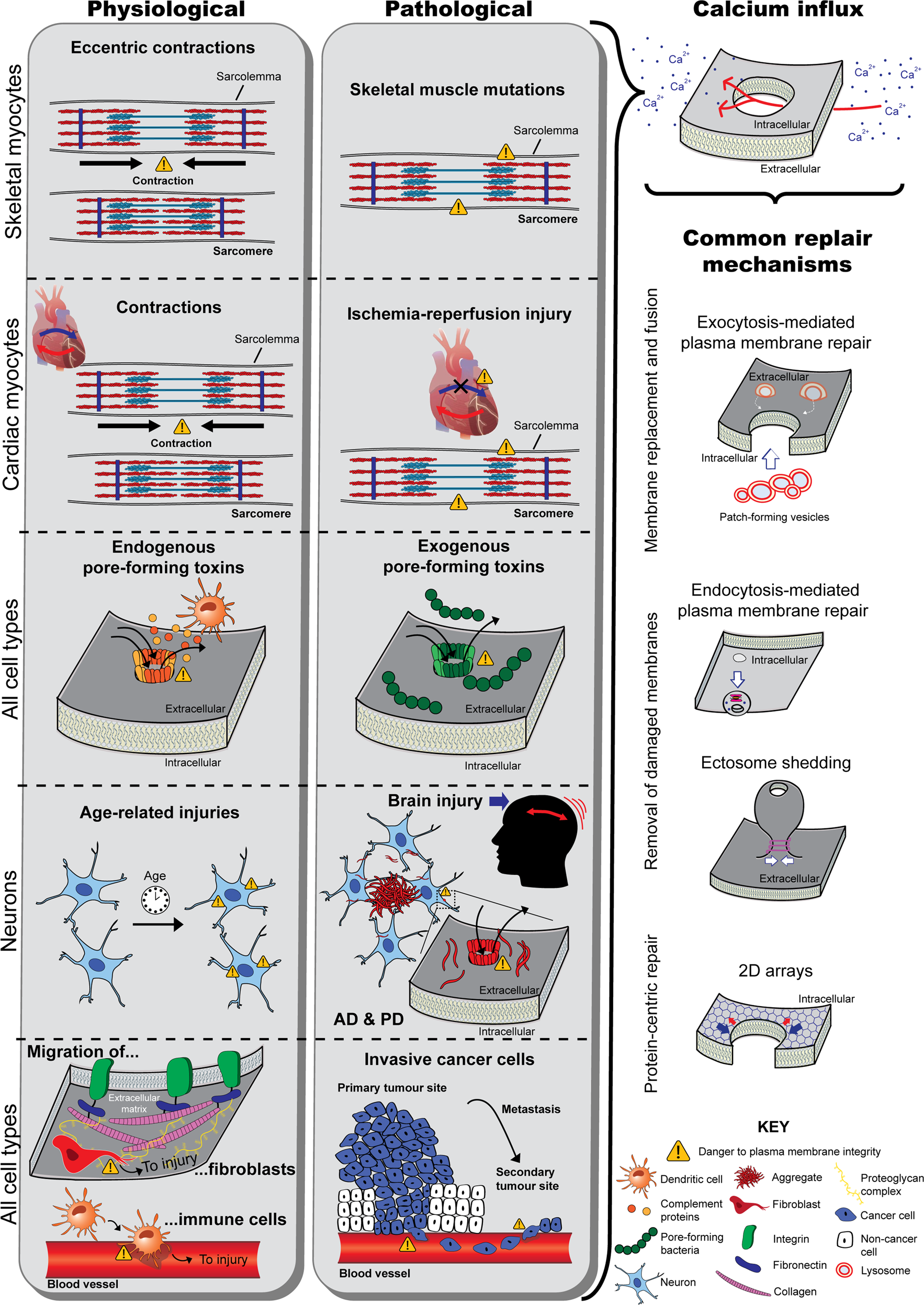
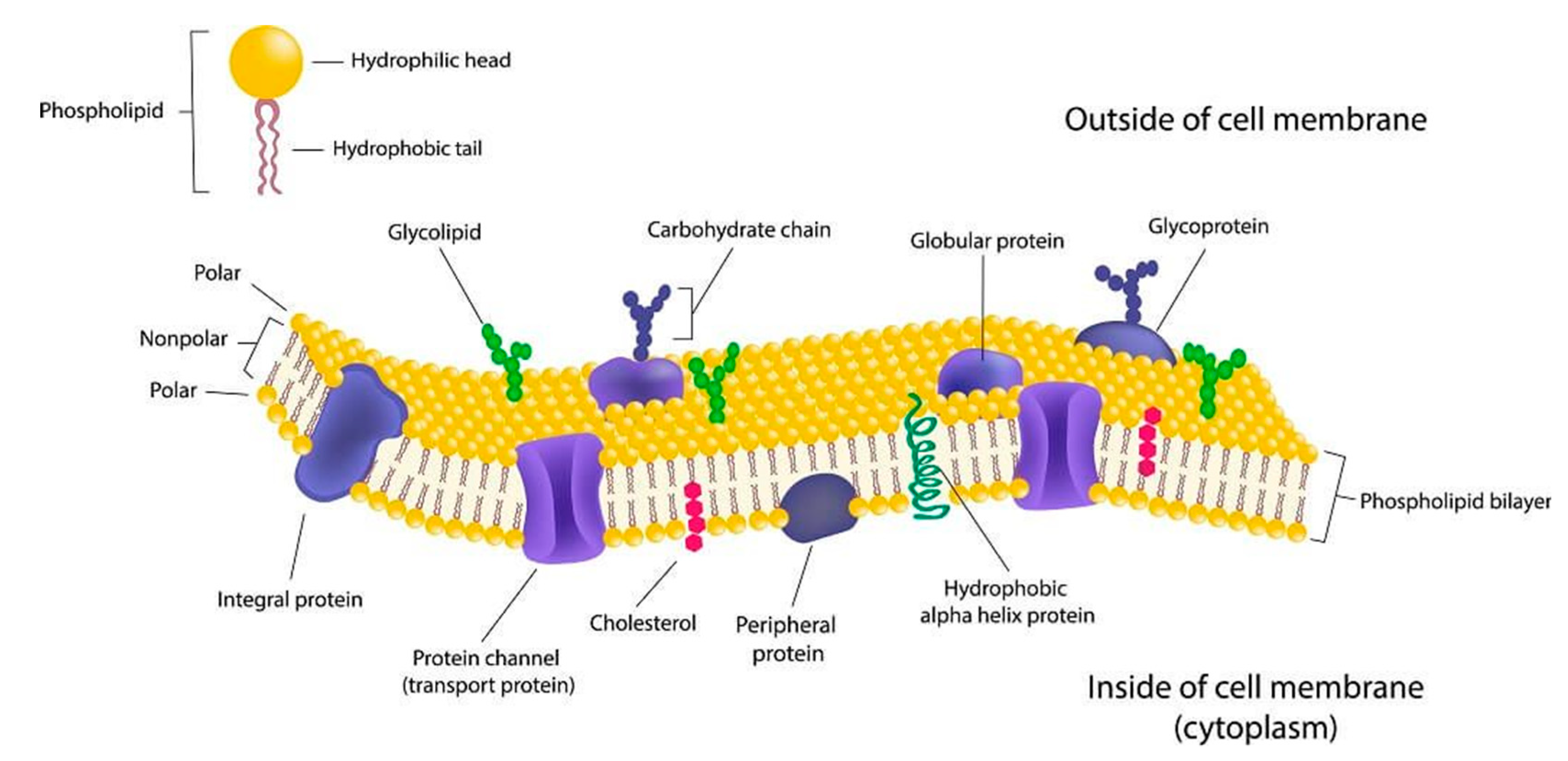
Original Research Cell membranes are commonly considered fundamental structures having multiple roles such as confinement storage of lipids sustain and control of membrane proteins. A cell cannot survive if it is totally isolated from its environment. The cell membrane plasma membrane is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell.
1 15 Amer Assoc Blood Banks Arlington VA 1986 Google Scholar. For the same token a bacterial toxin does not insert into the membrane through a nonlamellar phase nor two membranes fuse via a rhombohedral phase. Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals.
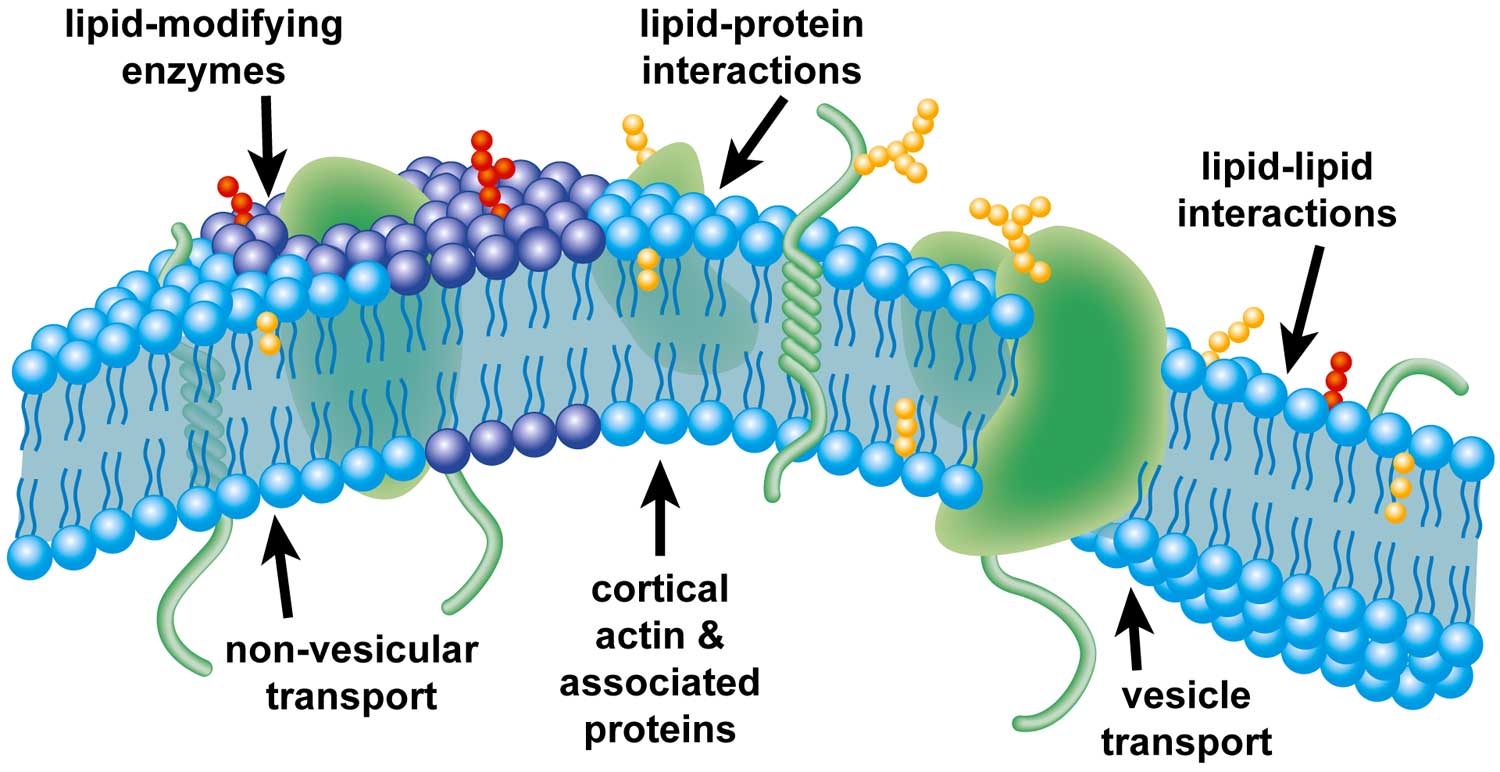
35Q30 92C50 74F10 1. The proteins and lipids in membranes form collectives the biology and physics of which will remain a challenge and a source for new insights in years to come. The fascination of membrane research is that the functionality of the cell membrane is dependent on the carefully orchestrated and mutually interdependent properties of lipids and proteins.
J D Robertson. Alexa Fluor Dye Conjugates. The paucimolecular unit membrane model of the structure of the plasma membrane is critically reviewed in relation to current knowledge of the chemical and enzymatic composition of isolated plasma membranes the properties of phospholipids the chemistry of fixation for electron microscopy the conformation of membrane proteins the nature of the lipid-protein bonds in membranes and possible mechanisms of transmembrane transport and membrane.
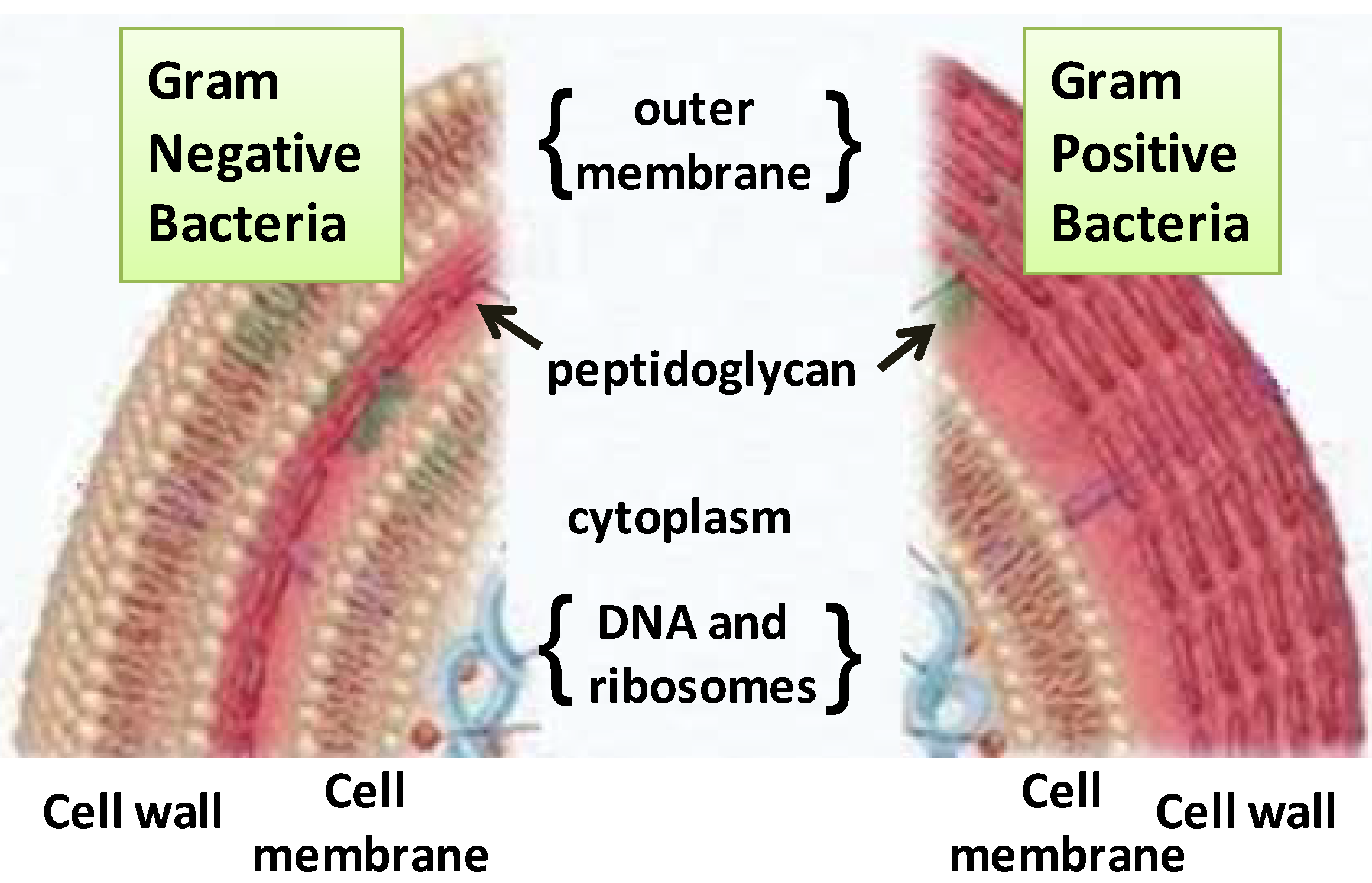
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. Red Cell Antigens and Antibodies ed. Ad Reveal the Subcellular Localization in Cell Imaging Applications.